|
|
|
Архитектура Астрономия Аудит Биология Ботаника Бухгалтерский учёт Войное дело Генетика География Геология Дизайн Искусство История Кино Кулинария Культура Литература Математика Медицина Металлургия Мифология Музыка Психология Религия Спорт Строительство Техника Транспорт Туризм Усадьба Физика Фотография Химия Экология Электричество Электроника Энергетика |
Task 4. Read the passage and do the given tasks.
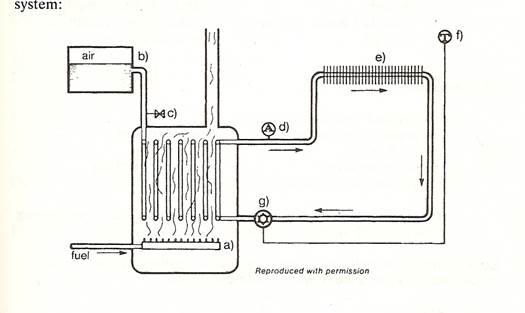
1.Study the following words. loop- кольцо, петля outlet-выпускное, выходное отверстие fin-1)радиаторная пластина 2) стабилизатор pump-насос, помпа valve-клапан, вентиль, заслонка One method of heating a building is to circulate hot water through radiators which are located in each room. The water is heated in a boiler by a burner and is kept at a constant temperature by a thermostat device called an aquastat. The aquastat is located on the outlet pipe from the boiler. The pipe runs in a continuous loop from the boiler to the radiators and back to the boiler. The function of a radiator is to transfer the heat from the hot water to the air in the room. Therefore they are made of a material which has the property of high thermal conductivity. The shape of the radiator is also important because the greater the surface area the more rapidly it gives off heat. One type of radiator, called a fin tube, consists of a number of thin fins shaped like a circle which are welded to a pipe passing through their centres. A thermostat in the room can be set to the required temperature. When the air temperature in the room decreases, the thermostat switches on the pump which is located on the return line from the radiators. When the room reaches the set temperature, the thermostat switches off the pump. An expansion tank is provided to allow for expansion of the water as it heats. A safety valve, located on the pipe leading to this tank, serves to relieve the pressure in the boiler if it is too high. 2. Now look at the diagram and match the letters with the parts of the heating system:
Answer these questions. a) What enables the inside of a building to be kept warm? b) Which part of the heating system circulates hot water through the continuous pipe? c) Which part acts as the room temperature controller? d) Which part functions as a means of controlling the temperature of the water in the boiler? e) Which part is designed to transfer the heat from the hot water to the air in the room? f) Which part prevents the boiler from blowing up? g) Which part serves as a device for heating the water in the boiler? h) Which part enables the water to expand safely?
4. Make true sentences by matching these halves of sentences:
Task 5. 1. Study the functions of an air conditioner: A temperature control B air cleaning C odour removal D germicidal treatment E noise control F air motion G relative humidity Air conditioners are designed so they are capable of performing some or all of the above functions. 2. Look at the following list of the most important functions for the following spaces, and make statements like the example below:
Auditoria ACE Commercial offices CBF Apartments ACE School classrooms ACD Motels AEC
Example: In an auditorium, the three most important functions of an air conditioner are to control the temperature, to remove odour and to control noise. 3. Now make similar statements about what you think to be the three most important functions of an air conditioner for the following spaces and discuss the reasons for your choice: Hospital patients' rooms Factory buildings Computer rooms Medical Buildings Hotel guests rooms 4. Look at the diagram of a packaged air conditioning unit. Read the dialogue between a student and a lecturer explaining how it works:
Afour-way adjustable louvre Bthermostat control and OFF-AIR-COOL switch CAjustable speed fan DFan motor EEvaporator FAir filters GFresh air opening at back HCondencer ICompressor
LECTURER: Here we have what's called a 'packaged air conditioning unit'. It's called that because it contains all its parts in one unit. Now I've removed the front of the cabinet so you can see inside. Notice that it is located on an outside wall so that fresh air can be drawn in here. O.K. Can you all see? The air then passes through these aluminium air filters ... STUDENT: What is the function of the air filters? LECTURER: Umm ... Well it does what it says - it filters the air removing the dust so ... STUDENT: SO that's why it's dirty. LECTURER: Err ... Yes, but you are able to remove the filters for cleaning. In fact this one should be cleaned as soon as possible. Err. Aahem. Yes, then the air passes through the evaporator and ... STUDENT: What does that do? LECTURER: Err ... Well. That serves the function of cooling the air. You see, a gas is circulated through the condenser here. That's a cooling device which turns the gas into a liquid. It then passes through a valve into the evaporator here where ... STUDENT: Where the liquid evaporates. LECTURER: Err ... Yes, that's right. The liquid expands into a gas and absorbs heat from the evaporator which ... STUDENT: Absorbs heat from the air. LECTURER: Yes. Now keep quiet will you and don't touch that. STUDENT: What is the evaporator made up of? LECTURER: Oh. The evaporator consists of cooling coils made of copper with aluminium fins. They are designed to absorb the maximum amount of heat. The cool clean air is now forced into the room through the adjustable louvre by ... STUDENT: A fan. LECTURER: Yes, the fan here. I'll switch it on now so you can see how it works. Stand back. Now look. I told you not to touch that ... (BANG)
Поиск по сайту: |