 |
|
|
Архитектура Астрономия Аудит Биология Ботаника Бухгалтерский учёт Войное дело Генетика География Геология Дизайн Искусство История Кино Кулинария Культура Литература Математика Медицина Металлургия Мифология Музыка Психология Религия Спорт Строительство Техника Транспорт Туризм Усадьба Физика Фотография Химия Экология Электричество Электроника Энергетика |
For the period of oscillations of scope without loads have
Replacing in expressions (14.13) are (14.15) the first elements by expression (14.16), get
Thus, dependences of squares of periods on the squares of the proper characteristic sizes after a theory must be linear. Thus segment which chops off a chart on wasp of ordinates (squares of periods) equals the square of period of oscillations of free scope, and does the tangent of angle of slope of graph depend on the coefficient of proportion k between a rotary-type moment and corner α (wonders formula (14.2)). Dependence is experimentally probed between the period of oscillations of T of turning pendulum and radius of cylinders (long pegs). A chart is built in the co-ordinates of T2 = f(R2) for cylinders, whether T2 = f(L2) for pegs. If a graphic will be lineal, then it high-quality confirms justice of theoretical formulas (14.17) and (14.18), and coinciding of values, which chop off this graphic on wasp of ordinates, with the square of period of scope in number confirm justice of these formulas. Except for it, on the tangent of angle of slope of the indicated graph it is possible to find a coefficient k, and more precisely relation of m/k2, and after a formula (14.19) to calculate the period of oscillations of Tk. If it a calculation value will be near to directly measured, it will confirm justice of theoretical formulas, and in particular, formulas (14.9).
Practical part
1.To plug a device in a network 220 V and to press the switch of „СЕТЬ '”. 2. To press the switch of “СБРОС”. Carefully to turn a scope to its fixing due to reaching of small flag by a 7 electromagnet 6. 3. To press a switch „ПУСК”. An electromagnet will release a scope, and it will begin to carry out turning oscillations. An electronic block will deduct the amount of full oscillations and time of oscillations. 4. When a number 9 will appear on the indicator of amount of oscillations, to press a switch “СТОП”. Upon termination of 10th oscillation stop-watch of stop. 5. To define the period of oscillations, dividing time into the amount of oscillations, that on 10. 6. To push back a switch “ПУСК”. To execute measuring of period of oscillations of Tr in obedience to points 2 ÷ 5 three times. To add results to the table 14.1.
Table 14.1
Measure a Vernier calipers the diameters of cylinder (length of peg) and ball. Carefully, not to cut a wire short, fasten a load in a scope. For this purpose to release nuts 11, to move a slat 10 up, how downward, that centrings dowels 14. 7. Got in openings on a load. To twirl nuts and clutch a load spirally 12. To fasten a cylinder along his axis, peg - athwart to the plane of scope. 8. Like points 2 ÷ 5 to measure the period of oscillations on once for all loads, including for a ball. To add the results of measurings to the table 14.2.
Table 14.2.
9. To build the chart of dependence of T2 = f(R2), or T2 = f(L2). To continue a chart to crossing with the axis of ordinates and on a segment which is chopped off on it, to define the square of period of oscillations of free scope 10. On lineal part of graphic (fig.14.2) a little rather one from the second to choose two points 1 and 2. To define their co-ordinates for to the axes, but not from a table. To find the tangent of corner φ to inclination of graphic by formula
or 11. After formulas (14.17), (14.20) for cylinders, or (14.18), (14.21) for pegs to calculate a numerical value
12. Putting the got value, and also mean value 13. To define the value of ordinate which is chopped off by the graphic T2 = f(R2). To compare this value to the square of period of oscillations of scope. 14. Draw conclusion that to implementation of laws of oscillations of the turning pendulum, and also about justice of formulas for the moments of inertia of cylinder, peg, ball.
Figure 14.3
Control questions
1. What is turning pendulum? 2. Make and write down differential equation of free harmonic oscillations of the turning pendulum. 3. Write down equation of oscillations, which is the decision of differential equation of harmonic oscillations. Draw the graph of this equation. 4. Write down formulas for a period and cyclic frequency of oscillations of the turning pendulum.
Literature
1. 1. Чолпан П.П. Фізика.- К.: Вища школа, 2003.- С.77-80. 2. Лапотинський І.Е., Зачек І.Р. Фізика для інженерів.- Львів: Афіша, 2003.- С. 3. Савельев И.В. Курс общей физики. - т.1, М.: Наука,1982.- С.196-199. 4. Трофимова Т.И. Курс физики.- М: Высшая школа, 1990.- С.222-223.
Translator: S.P. Lushchin, the reader, candidate of physical and mathematical sciences. Reviewer: S.V. Loskutov, professor, doctor of physical and mathematical sciences.
Approved by the chair of physics. Protocol № 6 from 30.03.2009 .
Поиск по сайту: |
 . (14.16)
. (14.16) , (14.17)
, (14.17) ~ L2 (14.18)
~ L2 (14.18) ~ R2. (14.19)
~ R2. (14.19)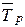 =
=
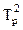 .
. , (14.20)
, (14.20) . (14.21)
. (14.21)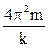 . (14.22)
. (14.22) , from a table 1 in a formula (14.19), calculate the square of period of oscillations of ball
, from a table 1 in a formula (14.19), calculate the square of period of oscillations of ball 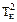 and compare it to directly measured (see a table 14.2).
and compare it to directly measured (see a table 14.2).