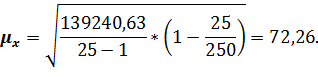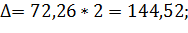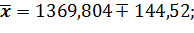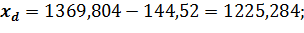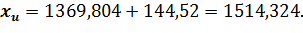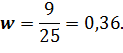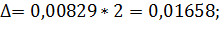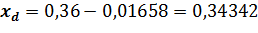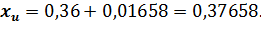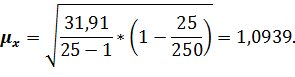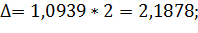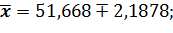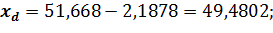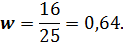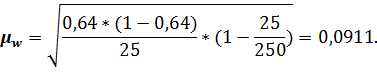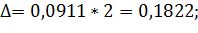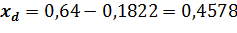|
|
|
Архитектура Астрономия Аудит Биология Ботаника Бухгалтерский учёт Войное дело Генетика География Геология Дизайн Искусство История Кино Кулинария Культура Литература Математика Медицина Металлургия Мифология Музыка Психология Религия Спорт Строительство Техника Транспорт Туризм Усадьба Физика Фотография Химия Экология Электричество Электроника Энергетика |
Calculation of variation indexes
The range of variance: · for the average selling price of poultry:
· for the cost of poultry:
· for fund of meat consumption to 1 person:
Mean linear deviation: · for the average selling price of poultry:
· for the cost of poultry:
· for fund of meat consumption to 1 person:
Dispersion: · for the average selling price of poultry:
· for the cost of poultry:
· for fund of meat consumption to 1 person:
Mean quadratic deviation: · for the average selling price of poultry:
· for the cost of poultry:
· for fund of meat consumption to 1 person:
Coefficient of variation: · for level of profitability:
· for selling price:
· for direct material costs:
Selective method As it was mentioned in the earlier paragraph already, statistical observation can be divided in two categories according to entirety of elements research process – continuous and non-continuous. Non-continuous, in its turn, also includes a few types, one of which is sampling observation. Sampling observation is observation at which the laws and characteristics of any general set are determined by the research of its certain part. The plurality of mathematical statistics methods which are used for proving and conclusion-making at the statistical observation is called the sampling method. The theoretical basis of the sampling method is the regularity of great numbers and the theory of probability. According to this basis, the differences between the similar characteristics of the general and the sampling sets can be reduced by increasing the quantity of sampling. The authentic and reliable estimation of the whole researched set due to the results of observation is possible only at a certain conditions, which are: the amount of sampled units of observation must be considerably great; the sampling of units for the sampling observation must provide each element of the set with equal possibility to get into the sampling; the purpose of the sampling method is to provide the true representation of the general set character and to estimate the meanings of its parameters. There are such kinds of sampling process: 1. Repeated sampling, at which each previously selected element returns to the general set and can be involved in sampling again. 2. Non-repeated sampling, at which each previously selected element does not return to the general set and doesn't take part in the following sampling. The main ways of sampling in the sampling set of elements are: 1. Casual method is the method of sampling set formation at which the selection of the general set elements is done in random order. 2. Mechanical sampling foresees the ranking of the general set by equal parts according to the natural arrangement of its units and the research of these units at equal intervals in an order they're arranged in the set. The mechanical sampling is always non-repeated. 3. Typical sampling foresees the division of the general set into homogenous typical groups with the further sampling due to the casual or the mechanical method. 4. Serial sampling foresees the selection of not the separate units of the general set but a certain series of them. In the sampling observation the nature of errors occuring is caused by that the sampling set of elements does not represent the general set exactly. As well as the sampling characteristic itself, the error of sampling is the casual value. The size of the casual error of sampling is determined due to the practical theorems of theory of probability. Error of sampling is an absolute value of difference between the sampling and the general characteristics. There are marginal and average errors of sampling. Average error of sampling is the divergence between the sampling and the general averages which does not exceed the size of the average squared deviation. The maximum of the possible divergence is called the marginal error of sampling (the error with the given degree of probability). There are two types of formulas for errors of sampling: one for the average and the other one for the particle (by method of repeated and non-repeated sampling). The errors for the average are determined by such formulas:
The errors for the particle are determined by such formulas:
The formula for determination of the sampling error at non-repeated sampling differs from the respective formula at the repeated sampling only by a multiplier It is proved by the theory of probability that the general characteristics do not decline from the sampling ones by the value which exceeds the value of the average fault of sampling and always equals 0,683 at the constant degree of probability ( The marginal error of sampling is connected with the average error of sampling by such equation:
where At the degree of probability 0,954, Organizing the sampling observation it is necessary to determine the quantity of the sampling set at which the margins of the possible error will not exceed a certain, previously given value. It is necessary to set such quantity of sampling which would provide the receiving of data for the complete reflection of the generalizing characteristics of the general set with the reliable degree of probability. The amount of sampling depends on such factors: 1. The size of the marginal error of sampling: the less the size of the given marginal error is, the greater the quantity of the sampling is. 2. The degree of the researched attribute variation: the greater the variation is, the greater the quantity of the sampling is. 3. The degree of reliable probability. The probability, in its turn, is connected with the normalized deviation. 4. The way of unit selection to the sampling set (repeated, non-repeated). Average error for the average:
Marginal error for the average:
The average error for the particle:
Marginal error for the particle:
For x2
Marginal error for the average:
The average error for the particle:
Marginal error for the particle:
Поиск по сайту: |

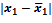
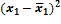
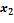
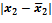
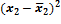


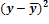
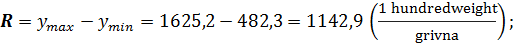
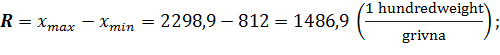

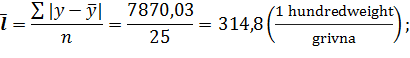

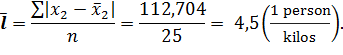
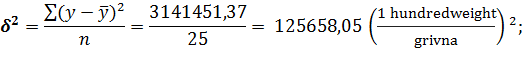
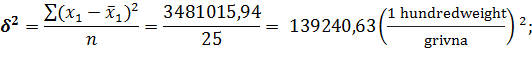
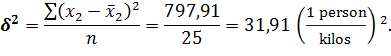
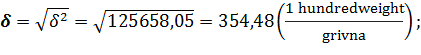



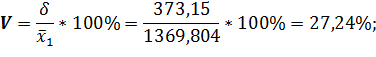
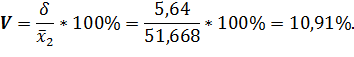
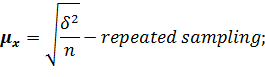

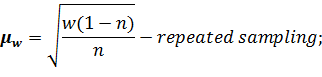
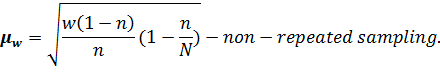
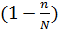 . It is caused by that at non-repeated sampling the elements do not return to the general set and thus its quantity decreases with time.
. It is caused by that at non-repeated sampling the elements do not return to the general set and thus its quantity decreases with time.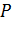 ). The probability of this statement can be increased by doubling or tripling the average error (
). The probability of this statement can be increased by doubling or tripling the average error ( 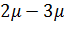 ). In this case the probability is 0,954 and 0,997 respectively.
). In this case the probability is 0,954 and 0,997 respectively.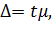
 – the normalized deviation which depends on the degree of probability.
– the normalized deviation which depends on the degree of probability. , at 0,997,
, at 0,997, 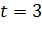 .
.