|
|
|
Архитектура Астрономия Аудит Биология Ботаника Бухгалтерский учёт Войное дело Генетика География Геология Дизайн Искусство История Кино Кулинария Культура Литература Математика Медицина Металлургия Мифология Музыка Психология Религия Спорт Строительство Техника Транспорт Туризм Усадьба Физика Фотография Химия Экология Электричество Электроника Энергетика |
Венетский язык (древний) 2 страница
[edit] History See also: History of the Republic of Venice [edit] Origins While there are no historical records that deal directly with the obscure and peripheral origins of Venice,[8] tradition and the available evidence have led several historians to agree that the original population of Venice consisted of refugees from Roman cities near Venice such as Padua, Aquileia, Treviso, Altino and Concordia (modern Portogruaro) and from the undefended countryside, who were fleeing successive waves of Germanic and Hun invasions.[9] Some late Roman sources reveal the existence of fishermen on the islands in the original marshy lagoons. They were referred to as incolae lacunae ("lagoon dwellers"). The traditional founding is identified with the dedication of the first church, that of San Giacomo at the islet of Rialto (Rivoalto, "High Shore"), which is said to have been at the stroke of noon on 25 March 421.[10][11] The last and most enduring immigration into the north of the Italian peninsula was that of the Lombards in 568, leaving the Eastern Roman Empire a small strip of coast in the current Veneto, and the main administrative and religious entities were therefore transferred to this remaining dominion, centered upon the Exarchate of Ravenna, the local representative of the Emperor in the East. The Venetian tradition of the islanders' aid to Belisarius was reported in early histories to explain the largely theoretical link to Ravenna, and to the Eastern Emperor. New ports were built, including those at Malamocco and Torcello in the Venetian lagoon. The tribuni maiores, the earliest central standing governing committee of the islands in the Lagoon, dated from c. 568.[12] The Venetians offered asylum to the Exarch Paul, who was in flight from the Lombard Liutprand.[13] Byzantine domination of central and northern Italy was subsequently largely eliminated by the conquest of the Exarchate of Ravenna in 751 by Aistulf. During this period, the seat of the local Byzantine governor (the "duke/dux", later "doge") was situated in Malamocco. Settlement on the islands in the lagoon probably increased in correspondence with the Lombard conquest of the Byzantine territories. Sometime in the first decades of the eighth century, the people of the lagoon elected their first leader Ursus, who was confirmed by Byzantium and given the titles of hypatus and dux.[14] He was the first historical Doge of Venice. In 775/776, the episcopal seat of Olivolo (Helipolis) was created. During the reign of duke Agnello Particiaco (811–827) the ducal seat was moved from Malamocco to the highly protected Rialto, the current location of Venice. The monastery of St. Zachary and the first ducal palace and basilica of St. Mark, as well as a walled defense (civitatis murus) between Olivolo and Rialto were subsequently built here. Winged lions, which may be seen throughout Venice, are a symbol for St. Mark. Charlemagne was initially hostile to Venice and sought to subdue the city to his own rule. He ordered the Pope to expel the Venetians from the Pentapolis along the Adriatic coast,[15] and Charlemagne's own son Pepin of Italy, king of the Lombards under the authority of his father, embarked on a siege of Venice itself. This, however, proved a costly failure. The siege lasted six months, with Pepin's army ravaged by the diseases of the local swamps and eventually forced to withdraw. A few months later Pepin himself died, apparently as a result of a disease contracted there. In the aftermath, an agreement between Charlemagne and Nicephorus recognized Venice as Byzantine territory and recognized the city's trading rights along the Adriatic coast. In 828, the new city's prestige was raised by the acquisition of the claimed relics of St. Mark the Evangelist from Alexandria, which were placed in the new basilica. The patriarchal seat was also moved to Rialto. As the community continued to develop and as Byzantine power waned, it led to the growth of autonomy and eventual independence. [edit] Expansion
Piazza San Marco in Venice, with St Mark's Campanile and Basilica in the background
These Horses of Saint Mark are a replica of the Triumphal Quadriga captured in Constantinople in 1204 and carried to Venice as a trophy. From the ninth to the twelfth century Venice developed into a city state (an Italian thalassocracy or Repubblica Marinara, the other three being Genoa, Pisa, and Amalfi). Its strategic position at the head of the Adriatic made Venetian naval and commercial power almost invulnerable. With the elimination of pirates along the Dalmatian coast, the city became a flourishing trade center between Western Europe and the rest of the world (especially the Byzantine Empire and the Islamic world). In the 12th century the foundations of Venice's power were laid: the Venetian Arsenal was under construction in 1104; the last autocratic doge, Vital II Michele, died in 1172. The Republic of Venice seized a number of places on the eastern shores of the Adriatic before 1200, mostly for commercial reasons, because pirates based there were a menace to trade. The Doge already carried the titles of Duke of Dalmatia and Duke of Istria. Later mainland possessions, which extended across Lake Garda as far west as the Adda River, were known as the "Terraferma", and were acquired partly as a buffer against belligerent neighbours, partly to guarantee Alpine trade routes, and partly to ensure the supply of mainland wheat, on which the city depended. In building its maritime commercial empire, the Republic dominated the trade in salt,[16] acquired control of most of the islands in the Aegean, including Cyprus and Crete, and became a major power-broker in the Near East. By the standards of the time, Venice's stewardship of its mainland territories was relatively enlightened and the citizens of such towns as Bergamo, Brescia and Verona rallied to the defence of Venetian sovereignty when it was threatened by invaders. Venice remained closely associated with Constantinople, being twice granted trading privileges in the Eastern Roman Empire, through the so called Golden Bulls or 'chrysobulls' in return for aiding the Eastern Empire to resist Norman and Turkish incursions. In the first chrysobull Venice acknowledged its homage to the Empire but not in the second, reflecting the decline of Byzantium and the rise of Venice's power.[17][18] Venice became an imperial power following the Venetian-financed Fourth Crusade, which in 1204 seized and sacked Constantinople and established the Latin Empire. As a result of this conquest considerable Byzantine plunder was brought back to Venice. This plunder included the gilt bronze horses from the Hippodrome of Constantinople, which were originally placed above the entrance to St Mark's cathedral in Venice, although the originals have been replaced with replicas and the originals are now stored within the basilica. Following the fall of Constantinople the former Roman Empire was partitioned among the Latin crusaders and the Venetians. Venice subsequently carved out a sphere of influence in the Mediterranean known as the Duchy of the Archipelago, and seized Crete. The seizure of Constantinople would ultimately prove as decisive a factor in ending the Byzantine Empire as the loss of the Anatolian themes after Manzikert. Though the Byzantines recovered control of the ravaged city a half century later, the Byzantine Empire was terminally weakened, and existed as a ghost of its old self until Sultan Mehmet The Conqueror took the city in 1453.
View of San Giorgio Maggiore Island from St. Mark's Campanile Situated on the Adriatic Sea, Venice always traded with the Byzantine Empire and the Muslim world extensively. By the late thirteenth century, Venice was the most prosperous city in all of Europe. At the peak of its power and wealth, it had 36,000 sailors operating 3,300 ships, dominating Mediterranean commerce. During this time, Venice's leading families vied with each other to build the grandest palaces and support the work of the greatest and most talented artists. The city was governed by the Great Council, which was made up of members of the noble families of Venice. The Great Council appointed all public officials and elected a Senate of 200 to 300 individuals. Since this group was too large for efficient administration, a Council of Ten (also called the Ducal Council or the Signoria), controlled much of the administration of the city. One member of the great council was elected "Doge", or duke, the ceremonial head of the city, who normally held the title until his death. The Venetian governmental structure was similar in some ways to the republican system of ancient Rome, with an elected chief executive (the Doge), a senate-like assembly of nobles, and a mass of citizens with limited political power, who originally had the power to grant or withhold their approval of each newly elected Doge. Church and various private properties were tied to military service, though there was no knight tenure within the city itself. The Cavalieri di San Marco was the only order of chivalry ever instituted in Venice, and no citizen could accept or join a foreign order without the government's consent. Venice remained a republic throughout its independent period and politics and the military were kept separate, except when on occasion the Doge personally headed the military. War was regarded as a continuation of commerce by other means (hence, the city's early production of large numbers of mercenaries for service elsewhere, and later its reliance on foreign mercenaries when the ruling class was preoccupied with commerce).
Francesco Guardi, The Grand Canal, 1760 (Art Institute of Chicago) The chief executive was the Doge, who theoretically held his elective office for life. In practice, several Doges were forced by pressure from their oligarchical peers to resign the office and retire into monastic seclusion when they were felt to have been discredited by perceived political failure. Though the people of Venice generally remained orthodox Roman Catholics, the state of Venice was notable for its freedom from religious fanaticism and it enacted not a single execution for religious heresy during the Counter-Reformation. This apparent lack of zeal contributed to Venice's frequent conflicts with the Papacy. In this context, the writings of the Anglican Divine, William Bedell, are particularly illuminating. Venice was threatened with the interdict on a number of occasions and twice suffered its imposition. The second, most famous, occasion in 1606, by order of Pope Paul V. Venetian ambassadors sent home still-extant secret reports of the politics and rumours of European courts, providing fascinating information to modern historians. The newly invented German printing press spread rapidly throughout Europe in the fifteenth century, and Venice was quick to adopt it. By 1482 Venice was the printing capital of the world, and the leading printer was Aldus Manutius, who invented the concept of paperback books that could be carried in a saddlebag. His Aldine Editions included translations of nearly all the known Greek manuscripts of the era.[19] [edit] Decline Venice's long decline started in the 15th century, when it first made an unsuccessful attempt to hold Thessalonica against the Ottomans (1423–1430). It also sent ships to help defend Constantinople against the besieging Turks (1453). After Constantinople fell to Sultan Mehmet II he declared war on Venice. The war lasted thirty years and cost Venice much of her eastern Mediterranean possessions. Next, Christopher Columbus discovered the New World. Then Portugal found a sea route to India, destroying Venice's land route monopoly. France, England and Holland followed them. Venice's oared galleys were at a disadvantage when it came to traversing the great oceans, and therefore Venice was left behind in the race for colonies. The Black Death devastated Venice in 1348 and once again between 1575 and 1577.[20] In three years the plague killed some 50,000 people.[21] In 1630, the plague killed a third of Venice's 150,000 citizens.[22] Venice began to lose its position as a center of international trade during the later part of the Renaissance as Portugal became Europe's principal intermediary in the trade with the East, striking at the very foundation of Venice's great wealth, while France and Spain fought for hegemony over Italy in the Italian Wars, marginalising its political influence. However, the Venetian empire was a major exporter of agricultural products and, until the mid-18th century, a significant manufacturing center. [edit] Military and naval affairs
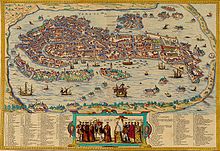
Historic map of Venice by Piri Reis By 1303, crossbow practice had become compulsory in the city, with citizens training in groups. As weapons became more expensive and complex to operate, professional soldiers were assigned to help work merchant sailing ships and as rowers in galleys. The company of "Noble Bowmen" was recruited in the later 14th century from among the younger aristocracy and served aboard both war-galleys and as armed merchantmen, with the privilege of sharing the captain's cabin. Though Venice was famous for its navy, its army was equally effective. In the 13th century, most Italian city states already were hiring mercenaries, but Venetian troops were still recruited from the lagoon, plus feudal levies from Dalmatia (the very famous Schiavoni or Oltremarini)[23] and Istria. In times of emergency, all males between seventeen and sixty years were registered and their weapons were surveyed, with those called to actually fight being organized into companies of twelve. The register of 1338 estimated that 30,000 Venetian men were capable of bearing arms; many of these were skilled crossbowmen. As in other Italian cities, aristocrats and other wealthy men were cavalrymen while the city's conscripts fought as infantry. By 1450, more than 3,000 Venetian merchant ships were in operation. Most of these could be converted when necessary into either warships or transports. The government required each merchant ship to carry a specified number of weapons (mostly crossbows and javelins) and armour; merchant passengers were also expected to be armed and to fight when necessary. A reserve of some 25 (later 100) war-galleys was maintained in the Arsenal. Galley slaves did not exist in medieval Venice, the oarsmen coming from the city itself or from its possessions, especially Dalmatia. Those from the city were chosen by lot from each parish, their families being supported by the remainder of the parish while the rowers were away. Debtors generally worked off their obligations rowing the galleys. Rowing skills were encouraged through races and regattas. Early in the 15th century, as new mainland territories were expanded, the first standing army was organized, consisting of condottieri on contract. In its alliance with Florence in 1426, Venice agreed to supply 8,000 cavalry and 3,000 infantry in time of war, and 3,000 and 1,000 in peacetime. Later in that century, uniforms were adopted that featured red-and-white stripes, and a system of honors and pensions developed. Throughout the 15th century, Venetian land forces were almost always on the offensive and were regarded as the most effective in Italy, largely because of the tradition of all classes carrying arms in defense of the city and official encouragement of general military training.
Venice, by Bolognino Zaltieri, 1565. The command structure in the army was different from that of the fleet. By ancient law, no nobleman could command more than twenty-five men (to prevent the possibility of sedition by private armies), and while the position of Captain General was introduced in the mid-14th century, he still had to answer to a civilian panel of twenty Savi or "wise men". Not only was efficiency not degraded, this policy saved Venice from the military takeovers that other Italian city states so often experienced. A civilian commissioner (not unlike a commissar) accompanied each army to keep an eye on things, especially the mercenaries. The Venetian military tradition also was notably cautious; they were more interested in achieving success with a minimum expense of lives and money than in the pursuit of glory. [edit] Modern age
A map of the sestiere of San Marco The Republic lost independence when Napoleon Bonaparte conquered Venice on 12 May 1797 during the First Coalition. The French conqueror brought to an end the most fascinating century of its history: during the 18th century Venice became perhaps the most elegant and refined city in Europe, greatly influencing art, architecture and literature. Napoleon was seen as something of a liberator by the city's Jewish population, although it can be argued they had lived with fewer restrictions in Venice. He removed the gates of the Ghetto and ended the restrictions on when and where Jews could live and travel in the city. Venice became Austrian territory when Napoleon signed the Treaty of Campo Formio on 12 October 1797. The Austrians took control of the city on 18 January 1798. It was taken from Austria by the Treaty of Pressburg in 1805 and became part of Napoleon's Kingdom of Italy, but was returned to Austria following Napoleon's defeat in 1814, when it became part of the Austrian-held Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia. In 1848–1849 a revolt briefly reestablished the Venetian Republic under Daniele Manin. In 1866, following the Third Italian War of Independence, Venice, along with the rest of the Veneto, became part of the newly created Kingdom of Italy. During the Second World War, the historic city was largely free from attack, the only aggressive effort of note being Operation Bowler, a precision strike on the German naval operations there in 1945. However the industrial areas in Mestre and Marghera and the railway lines to Padua, Trieste and Trento were repeatedly bombed.[24] On 29 April 1945 New Zealand troops under Freyberg reached Venice and relieved the city and the mainland, which were already in partisan hands.[25] [edit] Subsidence
Further information: Acqua Alta
Acqua Alta or high water in Venice.
Venice and surroundings in false colour, from Terra. The picture is oriented with North at the top. [edit] Foundations The buildings of Venice are constructed on closely spaced wooden piles. Most of these piles are still intact after centuries of submersion. The foundations rest on the piles, and buildings of brick or stone sit above these footings. The piles penetrate a softer layer of sand and mud until they reach a much harder layer of compressed clay. Submerged by water, in oxygen-poor conditions, wood does not decay as rapidly as on the surface. It is petrified as a result of the constant flow of mineral-rich water around and through it, so that it becomes a stone-like structure.[citation needed] Most of these piles were made from trunks of alder trees,[26] a wood noted for its water resistance.[27] The alder came from the western-most part of today's Slovenia (resulting in the barren land of the Kras region), in two regions of Croatia, Lika and Gorski kotar (resulting in the barren slopes of Velebit) and south of Montenegro.[citation needed] Leonid Grigoriev has stated that Russian larch was imported to build some of Venice's foundations.[28] Larch is also used in the production of Venice turpentine.[29] [edit] History
Panorama of the Giudecca Canal and the Saint Mark's Basin The city is often threatened by flood tides pushing in from the Adriatic between autumn and early spring. Six hundred years ago, Venetians protected themselves from land-based attacks by diverting all the major rivers flowing into the lagoon and thus preventing sediment from filling the area around the city. This created an ever-deeper lagoon environment. In 1604, to defray the cost of flood relief Venice introduced what could be considered the first example of a 'stamp tax'. When the revenue fell short of expectations in 1608, Venice introduced paper with the superscription 'AQ' and imprinted instructions, which was to be used for 'letters to officials'. At first, this was to be a temporary tax, but it remained in effect until the fall of the Republic in 1797. Shortly after the introduction of the tax, Spain produced similar paper for general taxation purposes, and the practice spread to other countries. During the 20th century, when many artesian wells were sunk into the periphery of the lagoon to draw water for local industry, Venice began to subside. It was realised that extraction of water from the aquifer was the cause. The sinking has slowed markedly since artesian wells were banned in the 1960s. However, the city is still threatened by more frequent low-level floods (called Acqua alta, "high water") that creep to a height of several centimetres over its quays, regularly following certain tides. In many old houses the former staircases used to unload goods are now flooded, rendering the former ground floor uninhabitable. Some recent studies have suggested that the city is no longer sinking,[30][31] but this is not yet certain; therefore, a state of alert has not been revoked. In May 2003 the Italian Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi inaugurated the MOSE project (Modulo Sperimentale Elettromeccanico), an experimental model for evaluating the performance of hollow floatable gates; the idea is to fix a series of 78 hollow pontoons to the sea bed across the three entrances to the lagoon. When tides are predicted to rise above 110 centimetres, the pontoons will be filled with air, causing them to float and block the incoming water from the Adriatic Sea. This engineering work is due to be completed by 2014.[32] [edit] Geography
Sestieri of Venice:
Aerial view of Venice
A rare tornado on June 12, 2012 seen from a window of the Venice Marco Polo Airport The city is divided into six areas or "sestiere". These are Cannaregio, San Polo, Dorsoduro (including the Giudecca and Isola Sacca Fisola), Santa Croce, San Marco (including San Giorgio Maggiore) and Castello (including San Pietro di Castello and Sant'Elena). Each sestiere was administered by a procurator and his staff. These districts consist of parishes – initially seventy in 1033, but reduced under Napoleon and now numbering just thirty-eight. These parishes predate the sestieri, which were created in about 1170. Other islands of the Venetian Lagoon do not form part of any of the sestieri, having historically enjoyed a considerable degree of autonomy. Each sestiere has its own house numbering system. Each house has a unique number in the district, from one to several thousand, generally numbered from one corner of the area to another, but not usually in a readily understandable manner. [edit] Climate According to the Köppen climate classification, Venice has a Humid subtropical climate (Cfa), with cool winters and very warm summers. The 24-hour average in January is 2.5 °C (36.5 °F), and for July this figure is 22.7 °C (72.9 °F). Precipitation is spread relatively evenly throughout the year, and averages 801 millimetres (31.5 in).
[edit] Economy
Поиск по сайту: |